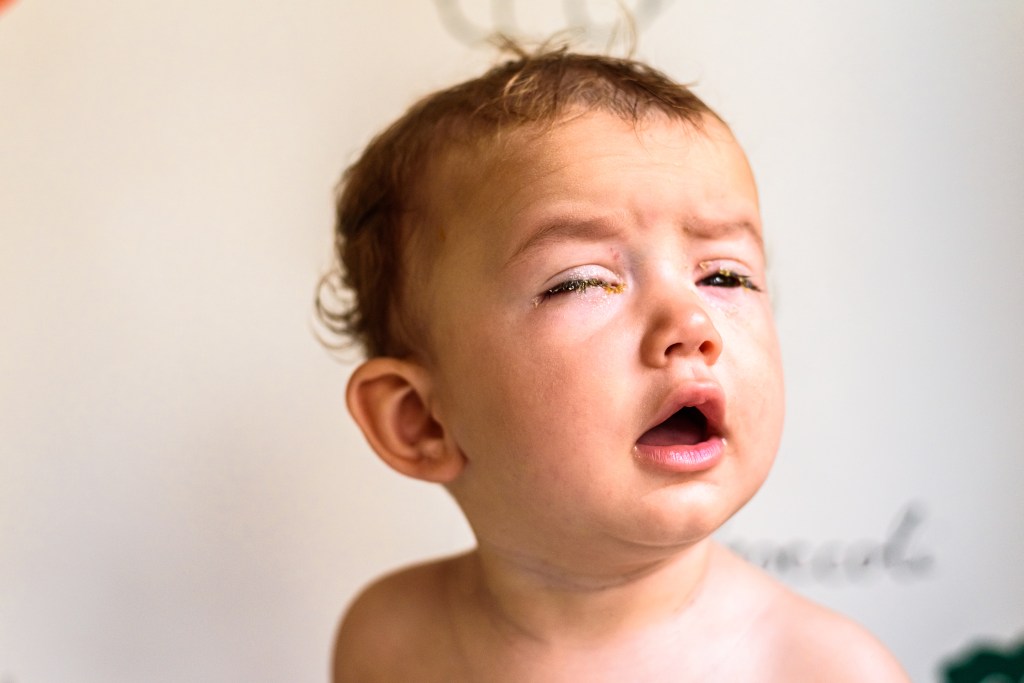
Pink eye (conjunctivitis) in babies can cause red, swollen, and watery eyes. It can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection, allergies, or irritants such as smoke or chlorine. It is important to seek medical advice to determine the cause and get proper treatment. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial conjunctivitis, while viral conjunctivitis usually clears on its own within 7 to 14 days. To help prevent the spread of pink eye, wash your hands frequently and avoid touching your eyes.
Is pink eye contagious?
Yes, pink eye is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person through direct contact with contaminated objects or through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing. It is important to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, to prevent the spread of pink eye.
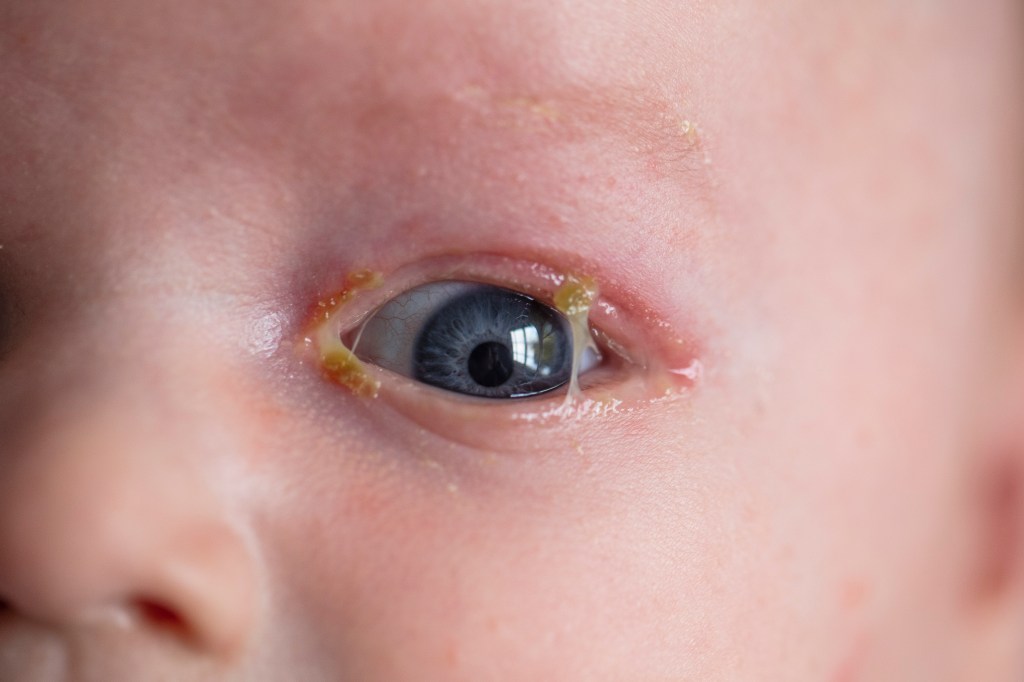
In babies and toddlers, the symptoms of pink eye may include:
- Red, swollen and/or watery eyes
- Eye discharge that can be yellow, green, or white in color
- Increased tear production
- Eye itching or burning sensation
- Eye sensitivity to light
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Crusting or sticky eyelashes upon waking
Treatments for pink eye in babies and toddlers may include:
- Artificial tears: Over-the-counter artificial tear drops can help relieve dryness and discomfort.
- Warm compresses: Placing a warm, damp cloth on the affected eye can help reduce swelling and discharge.
- Antibiotic ointments or drops: If the cause of the pink eye is a bacterial infection, your pediatrician may prescribe antibiotic ointments or drops.
- Antihistamine drops: If the cause of the pink eye is allergies, your pediatrician may prescribe antihistamine drops.
- Avoiding irritants: Try to keep your baby or toddler away from irritants, such as cigarette smoke, pet dander, and dust, which can make symptoms worse.
It is important to follow your pediatrician’s recommendations for treatment and to complete the entire course of medication, even if the symptoms have improved. Never use over-the-counter eye drops or ointments without consulting a pediatrician.
Pink eye can last anywhere from a few days to two weeks, depending on the cause and severity. In most cases, symptoms start to improve within a few days of treatment, but it is important to complete the full course of antibiotics or other prescribed medications to ensure full recovery. If the symptoms persist or worsen, it is best to seek medical advice.
Here are some steps you can take to prevent the spread of pink eye:
- Wash your hands frequently: Wash your hands with soap and water regularly, especially after touching your face, eyes, or any contaminated objects.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Don’t share towels, pillowcases, eye drops, or other personal items that may spread the infection.
- Disinfect surfaces: Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces like doorknobs, light switches, and faucet handles.
- Avoid touching your eyes: Touching your eyes with contaminated hands can spread the infection.
- Stay home: If you have pink eye, stay home from work, school, or daycare until you have been symptom-free for at least 24 hours and have started treatment.
- Use disposable tissues: When you sneeze or blow your nose, use disposable tissues and throw them away immediately.
By following these steps, you can help prevent the spread of pink eye to others in your family and community.
Pink eye is usually a mild condition, but in rare cases, it can become more serious. In some instances, it can lead to a more severe eye infection, corneal ulcers, or vision problems. If you suspect that your child or baby has pink eye and their symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical advice.
In general, pink eye in babies and toddlers takes about the same amount of time to clear up as in adults, which is usually within a few days to two weeks. However, the duration may vary depending on the cause and severity of the condition, as well as the response to treatment. Infants and young children are more prone to eye infections, so it’s essential to take proper care to prevent their spread and to ensure prompt treatment if they do occur.
